GMT time now |
|
20:11:19 Thu, 7 Aug 2025
|
| UTC Offset: UTC +0 |
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) operates at UTC+0 and serves as a foundational reference for global timekeeping. It is also known as "Zulu Time" (especially in aviation and military contexts), "Greenwich Time", or simply "GMT". GMT originated at the Prime Meridian (0° longitude) in Greenwich, London, and although Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) has become the official global standard for scientific accuracy, GMT remains widely used and recognized around the world.
Importance and Global Use of GMT
GMT holds historical significance as the world's first universal time standard, laying the foundation for the development of modern time zones. Its establishment enabled consistent scheduling across different regions, which was crucial for international trade, navigation, and communication, particularly during the expansion of railways and global shipping routes.
Today, GMT remains essential in various global sectors. Aviation, shipping, telecommunications, and financial markets continue to reference GMT (or UTC) for international coordination. It also plays a key role in computing systems, global data centers, and timestamping processes to ensure consistency across time zones. In some regions, GMT serves as the standard time during winter months, especially in areas that observe daylight saving time.
Where and When GMT is used worldwide
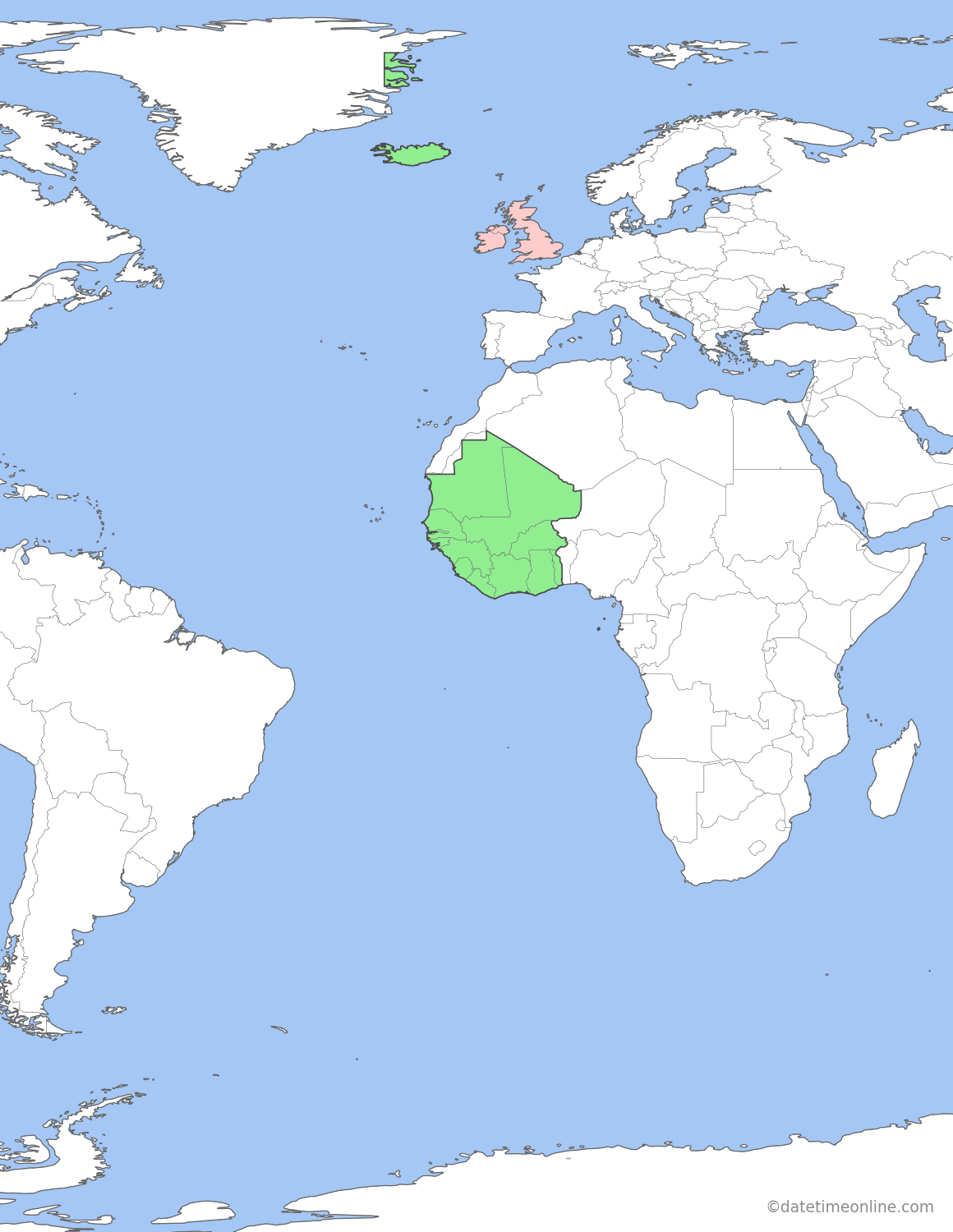
Follows GMT during parts of the year.
Operating on the same time (UTC +0).
Europe
European countries and territories using GMT during winter and BST during summer:
- Guernsey
- Isle of Man
- Jersey
- United Kingdom
European countries using GMT during winter and IST during summer:
- Ireland
European countries and territories using GMT all year:
- Greenland (Danmarkshavn)
- Iceland
Africa
African countries using GMT all year:
- Burkina Faso
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Ivory Coast
- Liberia
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Togo
Antarctica
Locations in Antarctica using GMT during summer and CEST during winter:
- Troll Station
Other Time Zones in UTC +0
Other time zones share the same offset as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), but are known by different names. While their clocks align, they may represent different regions or countries based on local time zone definitions.